SUD abbreviation – SUD (Substance Use Disorder) is a prevalent issue with severe consequences. Understanding its types, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into SUD, shedding light on its multifaceted nature and empowering individuals with the knowledge to address it effectively.
The term SUD encompasses a range of substance-related disorders, each with unique characteristics and symptoms. It’s a complex condition influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors, requiring tailored treatment plans and preventive measures.
1. Definition of SUD

Substance use disorders (SUDs) are a group of conditions characterized by compulsive drug use despite negative consequences.
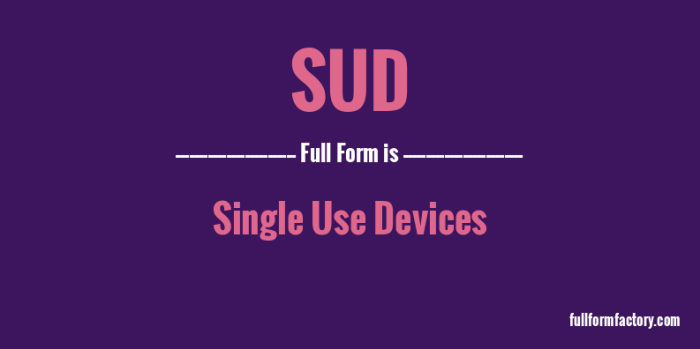
The acronym SUD refers to the full form “substance use disorder” and is commonly used in the context of mental health and addiction.
2. Types of SUDs
SUDs can be classified into different types based on the substance being abused:
- Alcohol use disorder: Involves excessive alcohol consumption leading to problems in relationships, work, and health.
- Opioid use disorder: Characterized by dependence on opioids, such as heroin or prescription painkillers.
- Cannabis use disorder: Involves excessive use of cannabis, leading to impairments in cognitive function and daily activities.
- Cocaine use disorder: Involves compulsive use of cocaine, resulting in problems with physical and mental health.
- Methamphetamine use disorder: Characterized by excessive use of methamphetamine, leading to addiction and severe health consequences.
3. Causes of SUDs: SUD Abbreviation
SUDs are caused by a complex interplay of factors:
- Biological factors: Genetics, brain chemistry, and physical health conditions can contribute to SUDs.
- Psychological factors: Mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, can increase the risk of SUDs.
- Social factors: Environmental influences, such as peer pressure, childhood trauma, and access to drugs, can play a role in SUDs development.
4. Diagnosis of SUDs
SUDs are diagnosed using specific criteria Artikeld in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5).
Assessment involves:
- Medical examination
- Substance use history
- Mental health evaluation
5. Treatment for SUDs
Treatment for SUDs aims to address the underlying causes and consequences of addiction.
Options include:
- Behavioral therapy: Focuses on changing thoughts and behaviors related to substance use.
- Medication: Can help manage cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and co-occurring mental health conditions.
- Support groups: Provide peer support and accountability.
- Inpatient treatment: Offers a structured and supervised environment for intensive treatment.
6. Prevention of SUDs
Prevention strategies aim to reduce the risk of SUDs development:
- Education: Raising awareness about the risks and consequences of substance use.
- Community initiatives: Promoting healthy activities and reducing access to drugs.
- Policy changes: Implementing laws and regulations to restrict substance availability and promote treatment.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, SUD is a serious public health concern that demands attention. By understanding its various aspects, we can work towards prevention, early intervention, and effective treatment. It’s essential to destigmatize SUD and foster a supportive environment where individuals can seek help without judgment.
Only through collective efforts can we create a society free from the devastating effects of substance use disorders.
FAQ Summary
What is the difference between SUD and addiction?
SUD is the clinical term for a substance use disorder, while addiction is a more general term that refers to a compulsive behavior or dependence on a substance.
Can SUD be cured?
SUD is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and support. While there is no cure, treatment can help individuals achieve recovery and maintain abstinence.
What are the most common types of SUD?
Alcohol use disorder, opioid use disorder, and cannabis use disorder are among the most prevalent types of SUD.